KardiaChain
Summary
As innovation and growth continues to progress for the blockchain industry, sharply growing demands have driven an increase in specialized cryptocurrencies that operates within their various niches. However, most blockchains’ operations and communications are limited to their own platform.
This limitation was quickly apparent, and a number of blockchain has been conceptualized in the race towards interoperability, such as Polkadot, Icon, Uniswap, or WanChain. And although they all share the common goal of uniting blockchain, each are unique in their own approach and methodology in achieving that goal.
KardiaChain, the newest member of the family, is no different. By utilizing dual-node technology, the platform aims to provide non-invasive, cross-chain communication with a chain of choice, both public and private.
The implementation would allow dApps to simultaneously access both ledgers of KardiaChain and its partner chain, increasing chain utility and exposure to a wider user base through interconnected smart contracts. It would also be possible to leverage the available resources across multiple chains for increased scalability and incorporate functions of various dApps to specific use cases.
Ultimately, KardiaChain’s goal is to provide a standardized multi-chain framework that can incorporate blockchains as modular components of the ecosystem, and facilitate communication and transfer of assets and data across multiple networks.
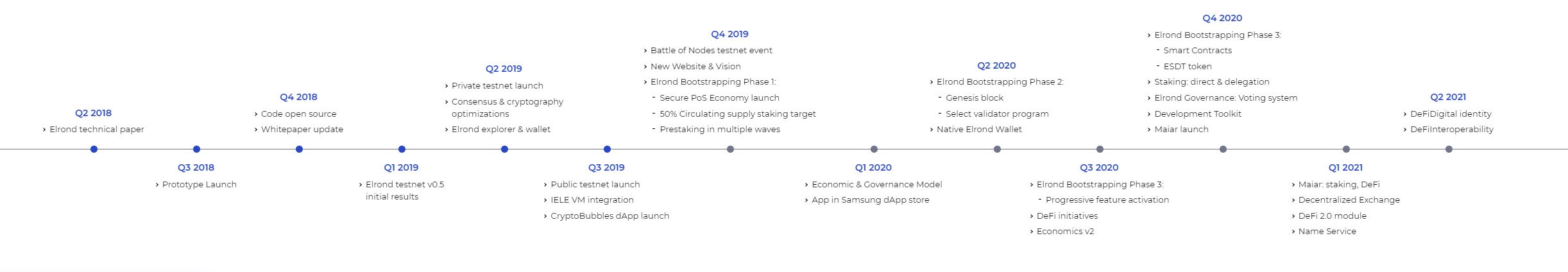
KardiaChain was first announced in October 2018, and its main net went live on December 29th, 2020. This is relatively recent, yet the project has already formed a number of partnerships, mainly with companies based in Southeast Asia, from eSports platform support with Theta Network to multiple societal applications. Examples include AI-powered data oracles with Oraichain, decentralized identity (DID) with Ontology, NFT adoption in real estate, e-commerce with Vecom and Fado, and certificate issuance with LG CNS.
Vietnam’s first VND-backed stablecoin will also be issued by VNDC on the KardiaChain platform, and will be swappable through the Nami exchange. VNDC’s Wallet Pro will allow users access to benefits and rewards that KAI membership offers such as investments, discounts, and Play&Earn rewards. Other features include opening credit lines by mortgaging KAI to create VNDC or USDT loans, P2P trading, VNDC Farming and Escrow.
KardiaChain has additionally formed strategic partnership with ViteX in order to foster user growth on the Decentralized Exchange. The collaboration will also allow Kardiachain to utilize Vite’s payment technology function as well. Vite will integrate KardiaChain’s unique interoperability to serve ViteX cross-chain transactions and work with KardiaChain’s mobile payment gateway with the top Vietnamese telco partners to enhance Vite’s user ecosystem.
The latest proposed partner chain is BSC, or Binance Smart Chain. The BSC-Kai Dual Node will be ready for demo on the KardiaChain testnet by the end of Q1 2021, and will be operable on mainnet in Q2 2021.
Fundamentals
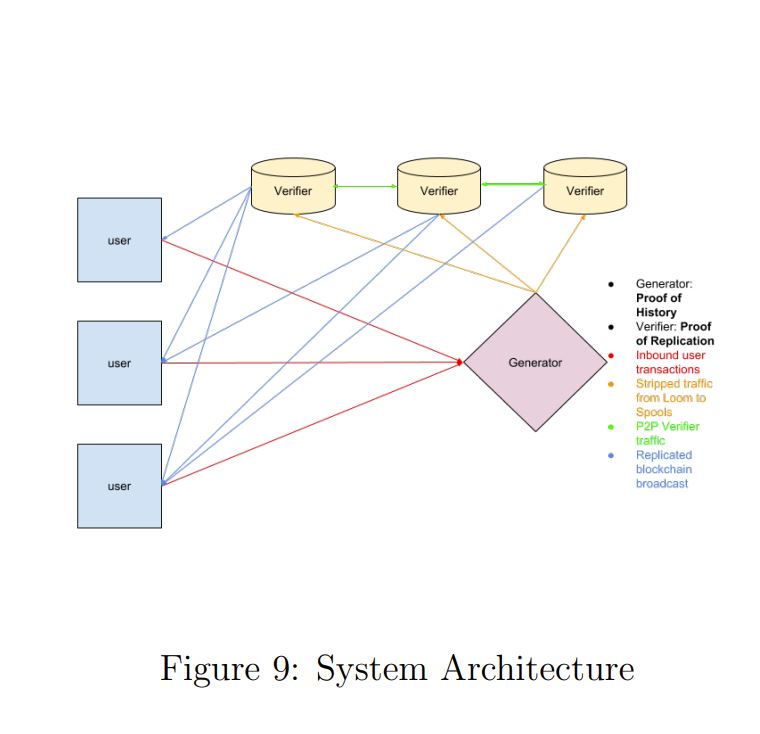
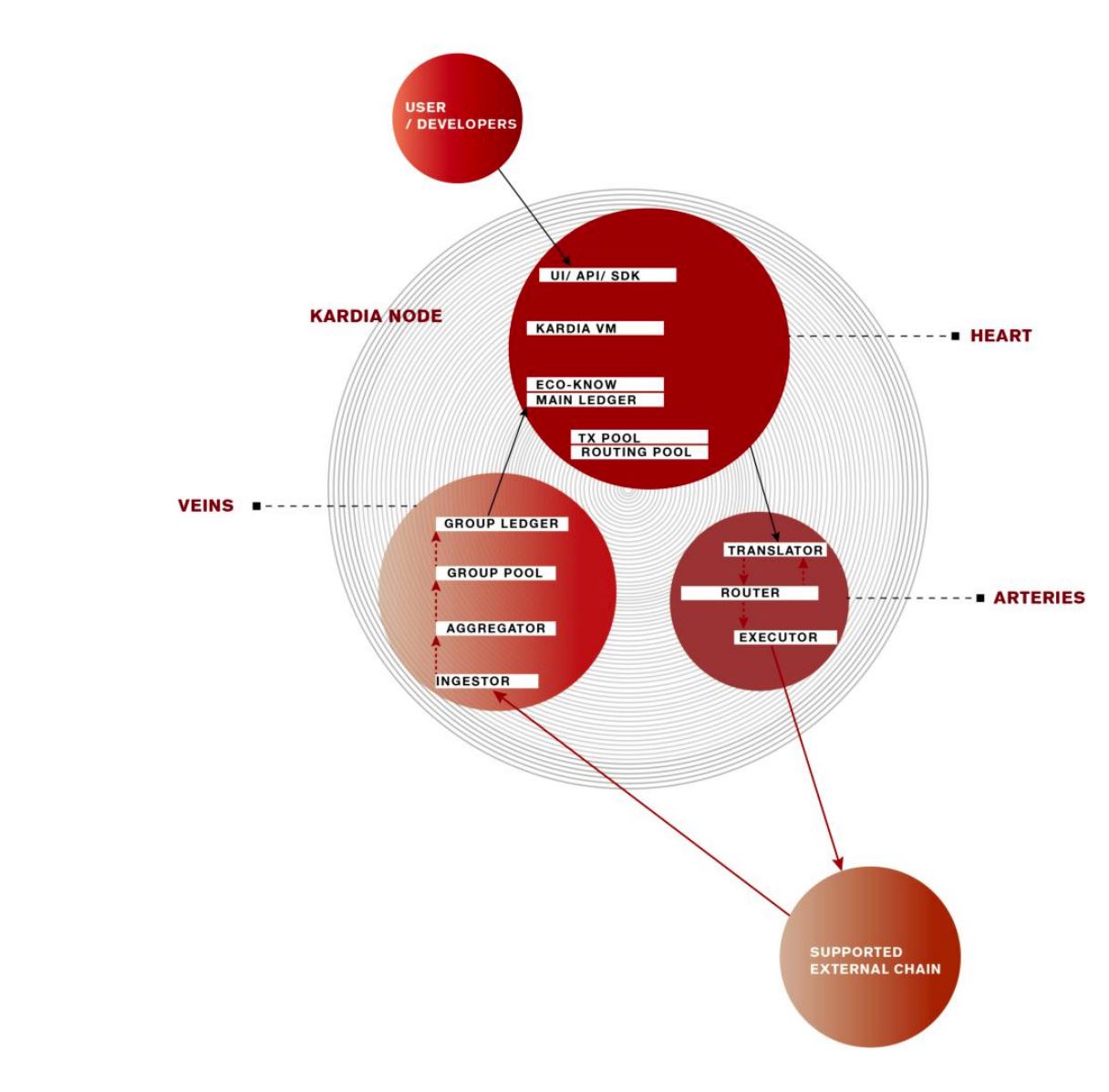
KardiaChain’s interoperability is achieved using the platform’s unique Dual Node concept, built upon three major components: Translator, Router, and Aggregator.
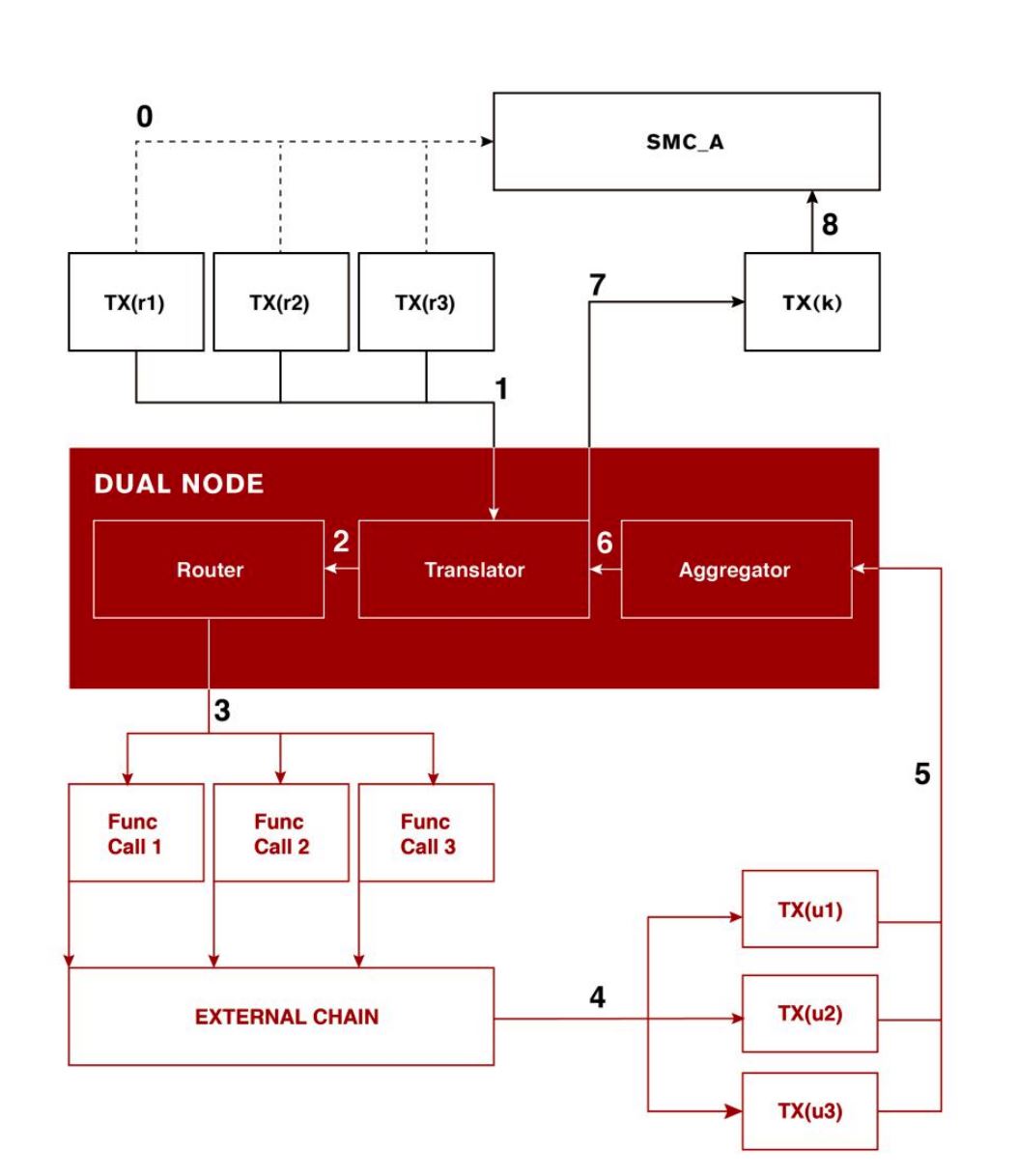
The Dual Master Nodes themselves have access to ledger data of two chains simultaneously, capable of receiving and updating cross-chain transactions, communications, and consensus. Interchain transaction data across KardiaChain are protected using the Schnorr Signature Algorithm multi-signature scheme.
The Translator component acts as a Rosetta Stone for the platform, utilizing Kardia’s unified Smart-Contract Language (KMSL) as a standardized programming language to enable compatibility across multiple different smart contract platforms.
The Router sorts Kardia’s traffic, and leveraging the most optimal chain onto which translated requests should be directed, depending on multiple variables such as current performance, fee, queue, and capacity.
Aggregator batches new updates from other chains to reduce resource strain on Kardiachain, at a ratio of one block of updates to one transaction on Kardiachain.
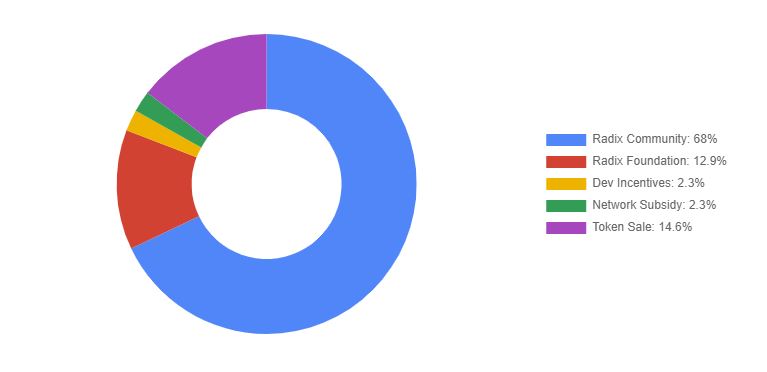
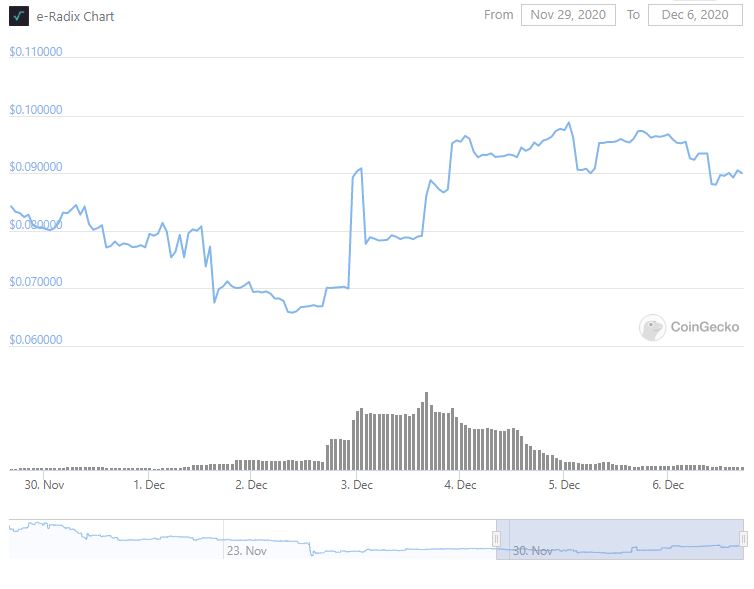
Token
KAI is currently trading at $0.1043 with a circulating supply of 2,049,800,000 and a max supply of 5,000,000,000 tokens. The current market cap is $213,461,949 USD with a 24hr volume of $5,369,180
.